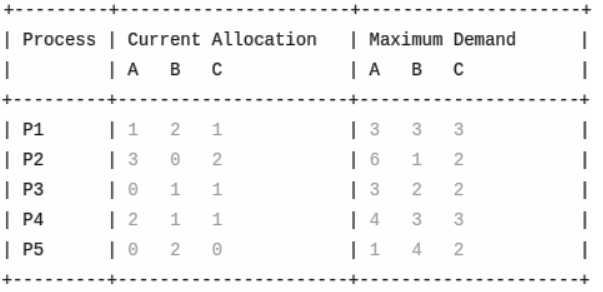
The total resources are (A,B,C) = (10,10,10). The total number of safe sequence possible are _____________
int flag[2];
int turn;
| |
void process0() {
flag[0] = 1;
turn = 1;
while (flag[1] && turn == 1) {
// busy wait
}
// critical section
flag[0] = 0;
// remainder section
}
|
void process1() {
flag[1] = 1;
turn = 0;
while (flag[0] && turn == 0) {
// busy wait
}
// critical section
flag[1] = 0;
// remainder section
}
|
flag[0] = 1;
turn = 1;
while (flag[1] && turn == 1) {
// busy wait
}
// critical section
|
bool function(bool *lock) {
bool old = *lock;
*lock = true;
return old;
}
|
bool lock = false;
void enter_critical_section() {
while (test_and_set(&lock)) {
// busy wait
}
// critical section
}
void leave_critical_section() {
lock = false;
}
|
bool lock = false;
void enter_critical_section() {
while (test_and_set(&lock)) {
// busy wait
}
// critical section
}
void leave_critical_section() {
lock = false;
}
|

The total resources are (A,B,C) = (10,10,10). The total number of safe sequence possible are _____________
Perform P(S) (wait operation) 5 times.
Perform V(S) (signal operation) 7 times.
Perform P(S) 3 more times.
Finally, perform V(S) 5 times.
The final value of S after these operations, considering the constraints of semaphore operations is _________