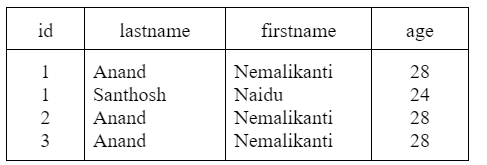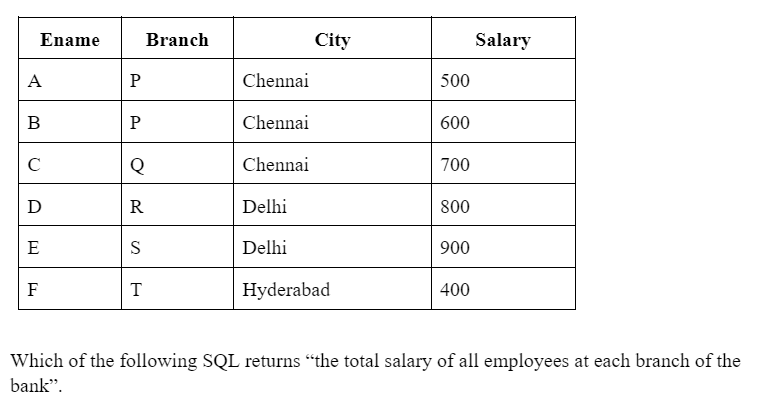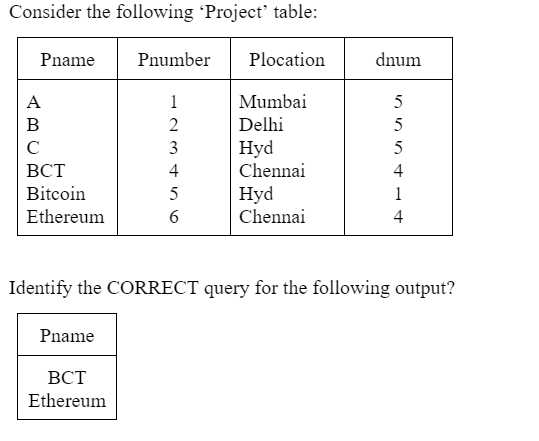
SELECT Pname FROM TABLE Project WHERE dnum=4;
SELECT Pname FROM Project FOR dnum=4;
SELECT Pname FROM TABLE Project FOR dnum=4;
SELECT Pname FROM Project WHERE dnum=4;
Correct Answer
Option 4
Solution
The given output will be retrieved by “SELECT Pname FROM Project WHERE dnum=4”.
Difficulty Level: 1
Positive Marks: 2.00
Negative Marks: 0.66