
[Note: Consider only 2 decimal points if it necessary]
Suppose we have a Single Source Shortest Path on the following Adjacency Matrix with vertex 0 as the source.
Find out the total cost for reaching all other vertices from the source node for which the shortest path distances are finalized____ ?
Alice got a message in combination of 1’s and 0’s. Alice needs to apply a huffman code algorithm to understand the given message.
110100110011011110101
Find the decrypted message sent by Bob is____? [ Hint: consider left node as 0 ]
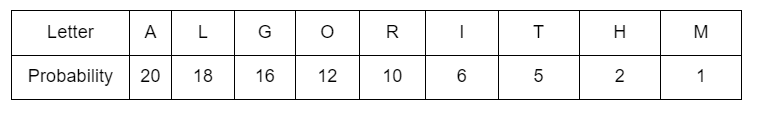
AAANNNAAAANNNDDDSSQ
A message of 100 characters over X is encoded using Huffman coding. Then the expected length of the encoded message in bits is____? [Note: Consider only 2 decimal points if it necessary]
I. It is often faster to add and remove edges from G when using an adjacency matrix.
II. Suppose that Dijkstra’s algorithm is run using a priority queue data structure for which insert and decrease key operations take O(log log V) time, extra-min operation take O(√V) time then the running time of Dijkstra’s algorithm on a directed weighted graph G = (V, E) containing non-negative edges will be O(V√V) + E log log V)
P: The sum of distinct weights of the minimum spanning trees obtained by Prim's and Kruskal's algorithm are always equal.
Q: In Huffman Coding, the item with the highest probability is always at the leaf that is closest to the root
R: Given a graph G = (V,E) with positive edge weights, the Bellman-Ford algorithm and Dijkstra’s algorithm can produce different shortest-path trees despite always producing the same shortest-path weights.